The Medicaid and CHIP Payment and Access Commission (MACPAC) is a nonpartisan agency in the legislative branch that analyzes policy and makes recommendations to federal and state-level policymakers. In this report, MACPAC provides an overview of the federal government’s role in providing health care to American Indians and Alaska Natives (AI/AN), including the structure of the Indian Health Service and the special Medicaid rules and protections that apply to AI/AN beneficiaries and Indian health providers.
CDC: Trends in Drug and Synthetic Opioid Overdose Deaths
In the February 12 issue of its Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report an increase in overdose deaths involving synthetic opioids other than methadone, cocaine, and psychostimulants. During the period studied, 2013 – 2019, synthetic opioid deaths largely consisted of illicitly manufactured fentanyl. In 2019, a total of 70,630 drug overdose deaths occurred, an increase of 4.3 percent over deaths in 2018.
CDC: Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Pandemic-Related Stress
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that Hispanic adults reported a higher prevalence of symptoms of depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. Estimates of self-reported suicidal thoughts/ideation among Hispanic persons (22.9%) were four times those among non-Hispanic Black (Black) persons (5.2%) and White persons (5.3%) and approximately twice those of multiracial and non-Hispanic persons of other races/ethnicities (8.9%).
Final Recommendation Statement: Screening for Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) released a final recommendation statement on screening for asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. The Task Force continues to recommend against screening in adults. View the recommendation, the evidence on which it is based, and a summary for clinicians, here.
Why Do Women Physicians Leave Practice?
Research shows that almost 40 percent of women physicians go part-time or leave medicine altogether within six years of completing their residencies. This is of particular concern in primary care, which has a higher percentage of female physicians. How can you address this problem? This article from the American Association of Medical Colleges looks at what is behind the early exodus and what pioneering institutions are doing to address it.
Study Finds 40% of U.S. COVID-19 Deaths Could Have Been Prevented
A new study by the Lancet Commission on Public Policy and Health in the Trump Era concludes that about 40 percent of the nation’s coronavirus deaths could have been prevented if the average death rate in the U.S. matched other industrialized nations. While the report faulted former President Trump’s “inept and insufficient” response to COVID-19, it said the roots of the nation’s poor health outcomes are much deeper. Read more.
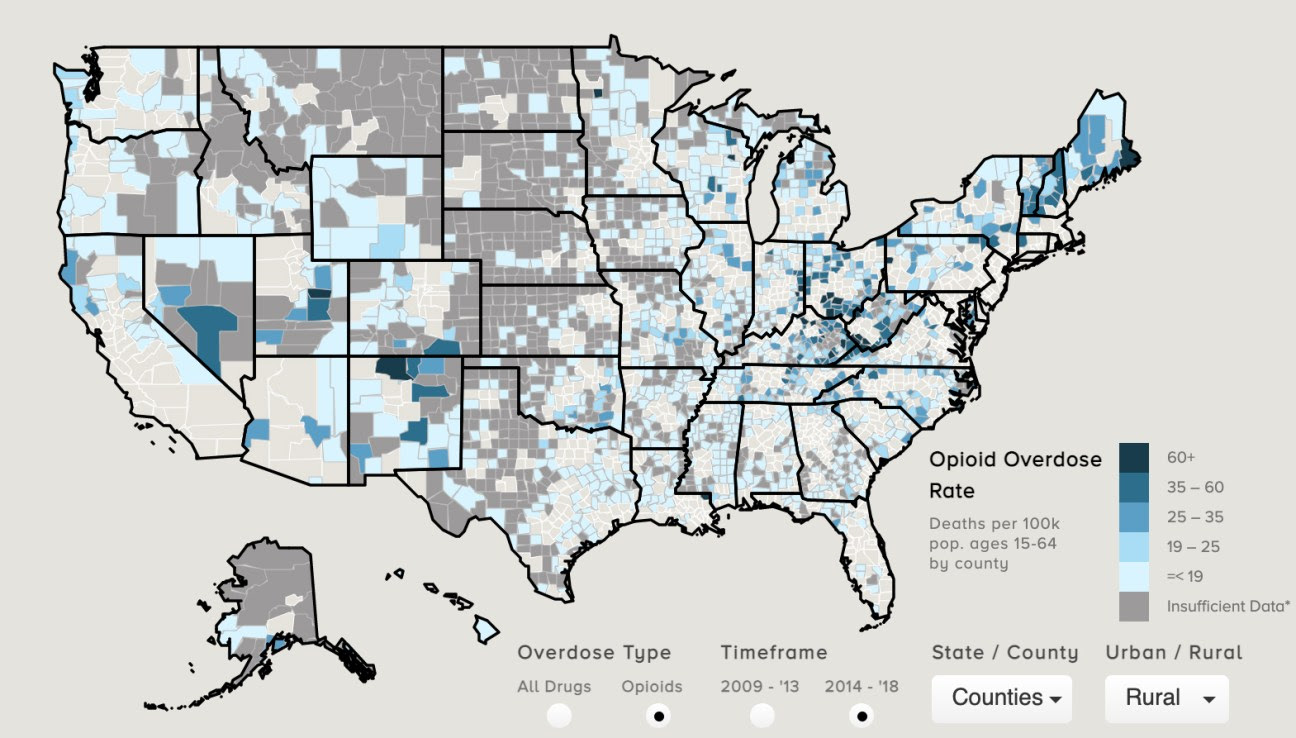
Report: 10 Western States See Some Drug Overdoses Deaths Increase by Nearly 100%

By Liz Carey
The Covid-19 pandemic-related stress, isolation, and a wave of drugs contaminated with extremely potent synthetic opioid, fentanyl, are factors in a severe rise of deadly overdoses.
Read more
New Research on the Intersection of Pregnancy-Associated Deaths and Intimate Partner Violence
New research examines the three leading causes of pregnancy-associated deaths, describes evidence-based approaches and strategies for prevention and intervention, and makes recommendations for further research.
The research is published in the February 2021 Journal of Women’s Health Special Issue: Maternal Morbidity and Mortality.
The special issue provide a comprehensive review of relevant literature, including biological and physiological risk factors, external risk factors, social determinants of health, and proven and potential interventions.
Sabrina Matoff-Stepp, Ph.D., in HRSA’s Office of Planning, Analysis, and Evaluation and colleagues from NIH, Johns Hopkins University, and the University of Virginia collaborated on the research.
Read the article published in the Special Issue.
Cost-Effectiveness of the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program
This month, HRSA published a pair of manuscripts demonstrating the cost-effectiveness of the Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program (RWHAP) in the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes (JAIDS).
These two papers present findings from the first formal evaluation of the RWHAP’s cost-effectiveness at a national level. The first paper presents a new and innovative mathematical model that can be used as a tool for estimating the cost-effectiveness of the RWHAP under a variety of policy scenarios and assumptions. The second paper compares estimated health care costs and outcomes over a 50-year period in the presence of the RWHAP relative to those expected if the comprehensive and integrated system of medical and support services funded by the RWHAP were not available.
Read the first paper.
Read the second paper.
Cancer Disparities among Rural Racial/Ethnic Minorities in U.S.
New research from the University of South Carolina shows that rural Black populations have the highest cancer mortality rate in the U.S.
The report, published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, also indicates cancer mortality rates among rural White and Black populations exceed those of their urban counterparts. The report summarizes how racism and social determinants of health disproportionately affect rural racial/ethnic minorities, examining cancer disparities in particular, and offers recommendations to reduce them. The research was funded by HRSA in collaboration with the National Cancer Institute.
